A Student’s Perspective on STEM Education: A Blog Series
Throughout the summer, AYVA will be launching a blog series all about the use of technology in STEM education.
 My name is Katrina and I started at AYVA in January as a co-op student from the University of Guelph. I am a Biological and Pharmaceutical Chemistry major and STEM education has always been something that I am passionate about. I feel like I am in a unique position to help improve it through AYVA as a student who has recently experienced secondary science education and is currently studying science in university. I have some perspective on how technology can be used to improve learning having used PASCO technology both in high school and university.
My name is Katrina and I started at AYVA in January as a co-op student from the University of Guelph. I am a Biological and Pharmaceutical Chemistry major and STEM education has always been something that I am passionate about. I feel like I am in a unique position to help improve it through AYVA as a student who has recently experienced secondary science education and is currently studying science in university. I have some perspective on how technology can be used to improve learning having used PASCO technology both in high school and university.
Through this series, I will be covering some successes, issues, and perspectives on the status of STEM education in Canada along with my personal experiences as a STEM student in Canada.
Why does this series matter?
I am one example of how good teaching can truly inspire a student to pursue science and can make a significant impact on their educational choices and career path.
I was very fortunate to go to a high school in the Dufferin-Peel Catholic School Board that had an incredible science department. In that department, I have had various role models and mentors who helped me realize what I wanted to do.
Through these teachers, I have had so many opportunities to confidently pursue science. They helped me attend STEM outreach camps, provided extra help and resources, let me into their classroom after class hours to talk about advanced topics and issues in science.
My high school mentor helped my friend and me to pursue a graduate-level research project at the University of Guelph while we were still in grade 12 for a competition. How many people could say that they did that at 17? I owe a lot to my teachers for helping me achieve my goals and for guiding me to where I am today.
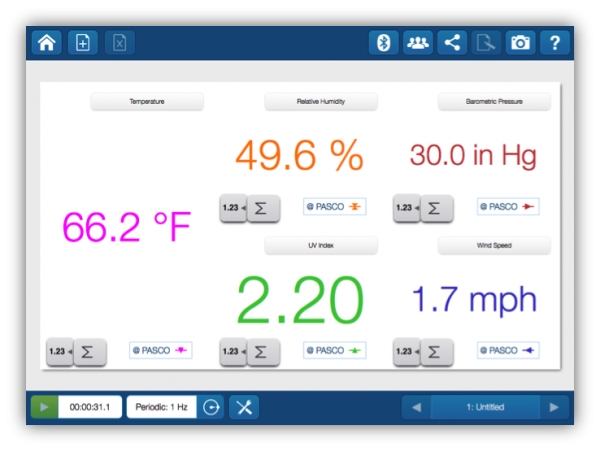
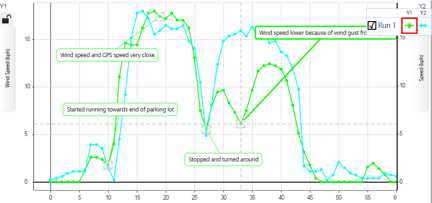
I also attended a high school that was relatively new and as such had many resources available for inquiry learning. We had SmartBoards, laptop carts, and PASCO equipment for our science department. This technology helped supplement my lessons and made me understand some more difficult concepts. The PASCO equipment in particular helped me quite a bit in my physics classes – it was the only class where I never fully grasped concepts until I did the experiments.
With that being said, I know that not everybody has access to a good science education. I know that I am fortunate to have gone to a school with teachers that have the resources to ensure that their students succeed. This is why I am writing this series – I want to highlight some of the key issues in STEM education and give insight using my own experiences. Through this, I hope that I can inspire others to push for better and accessible STEM education.