Description
Overview
The Wireless Motion Sensor connects via Bluetooth or USB to your device and uses ultrasound to measure the position, velocity, and acceleration of objects. This enables students to take turns measuring themselves, while the class observes their motion materializing as a graph in real-time. The sensor can detect objects ranging from 15 cm to 4.0 m away, and without cables to get in the way, students can explore handheld and ceiling-mounted applications.
Features
- Measures position, velocity, and acceleration
- False Target Rejection Technology produces cleaner data
- Clips directly to PASCO Dynamics Tracks
- Rod clamp for mounting
- 180° pivoting head
- Rechargeable lithium-ion battery
- Bluetooth® or USB connectivity
Applications
- Measure the motion of moving objects
- Explore the relationship between position, velocity, and acceleration
- Measure objects in freefall
- Measure how air resistance affects falling objects
- Investigate frames of reference
- Investigate the Conservation of Energy and Momentum
- Simple harmonic motion
- Seafloor mapping
How It Works
The Wireless Motion Sensor uses echolocation, similar to a dolphin or bat. In order to determine the distance to an object, an ultrasonic pulse is emitted from the sensor. The sensor listens for a signature ‘echo’ which reflects off the object’s surface. The object’s distance is calculated by determining the elapsed time between the ultrasonic pulse and detected echo, then, this value is used with the speed of sound to calculate the object’s distance. Measurements of velocity and acceleration are derived algorithmically using numerical methods. This provides a balanced approach to calculating numerical derivatives, which reduces noise and minimizes smoothing effects on high-frequency peaks.
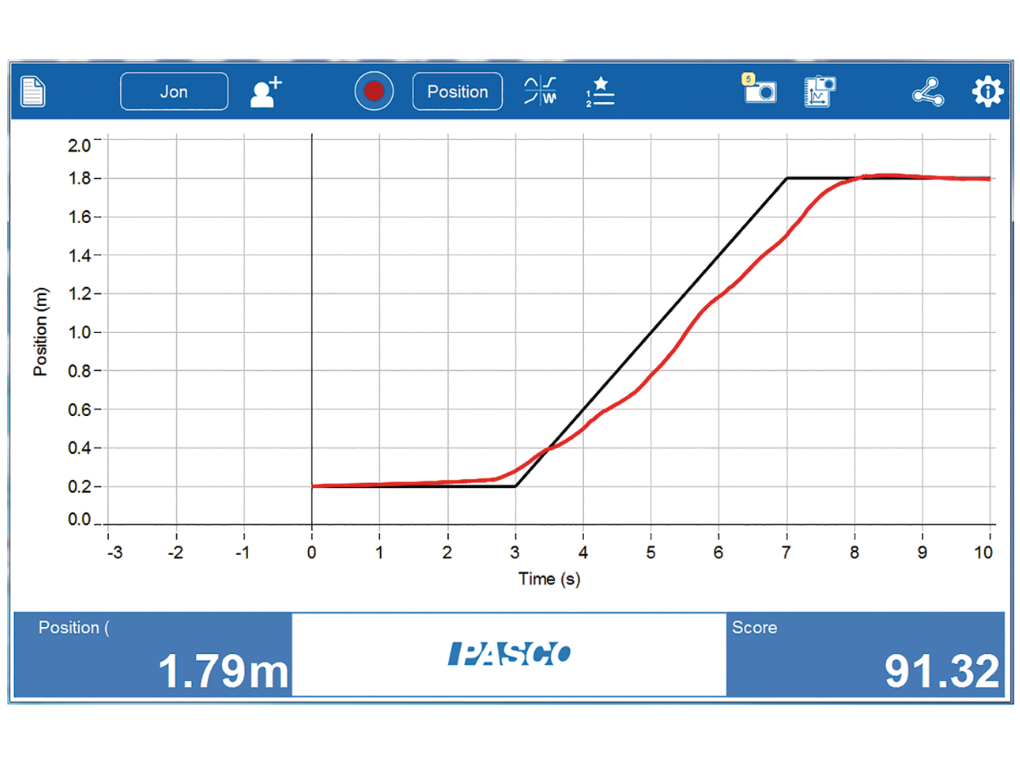
The Wireless Motion Sensor is also ideal for use with our free MatchGraph! software, an ideal way to teach the concepts of motion, motion graphing and rate of change or slope.
Product Specifications
| Range | 0.15 to 4 m |
| Resolution | 1 mm |
| Maximum sample rate | 50 Hz |
| Transducer rotation range | 180° |
| Rechargeable battery | Lithium-polymer |
| Connectivity | Direct USB or via Bluetooth (Bluetooth 4.0) |
Battery and Logging
| Stored Data Points Memory (Logging) 1 | Not Supported |
| Battery – Connected (Data Collection Mode) 2 | >20 hr |
| Battery – Logging (Data Logging Mode) 3 | Not Supported |
| Battery Type | LiPo |
1 Minimum # of data points with all measurements enabled, actual results depend on enabled measurements.
2 Continuous use in a connected state until battery failure, actual results will depend on sample rate, active measurements, and battery condition.
3 Logging until battery failure, actual results will depend on sample rate, active measurements, and battery condition.
* Normal classroom use is the sensor in active use for 20min/lab for 120 lab periods/yr.
Experiment Library
Perform the following experiments and more with the Wireless Motion Sensor.
Visit PASCO’s Experiment Library to view all activities for this product.
Near and Far
In this lab, students use a motion sensor to describe the position of an object as being near or far from another object. This lab will help students recognize that an object in motion changes its position.
Acceleration and Gravity
In this activity, students will use motion sensors to analyze how gravity affects the motion of falling objects varying in size and mass.
Newton’s Second Law
In this lab, students will use force and motion sensors to study the relationship between the net force applied to an object, the acceleration of the object, and the object’s mass.
Relative Motion
In this lab, students will use motion sensors to apply the concepts of relative motion and frames of reference to understanding velocity as a vector quantity in one-dimensional motion.
Position: Match Graph
Use a motion sensor to introduce the concept of representing motion as a change of position in a graphical form.
Work and Energy
In this lab, students will use motion and force sensors to develop an understanding of the work-energy theorem that relates the work done on an object by a net force to the change in the object’s kinetic energy.
Supporting Documents
| Manuals | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Wireless Motion Sensor Manual | English | 1.19 MB | |